
With Barcelona playing host to the QS Higher Ed Summit: Europe recently, we have taken a deep dive into Spain’s higher education sector.
The background
The latest data from Spain’s Ministerio de Universidades shows a significant post-pandemic recovery, with international student enrolments growing nearly 30% between the 2019/20 academic year, and 2021/22 – the most recent data available. European students remain well represented among international enrolments in Spanish universities, with Italy, France, Germany, and Romania all ranking in the top ten.
With data from 2021 to now, the QS International Student Survey 2024 reveals that overall interest in studying in Spain remains strong but steady. However, there is a noticeable increase in interest from students in Africa, the Middle East, and Asia Pacific. Interest from Western European students has slightly declined.
What students want from their Spanish study experience

Clearly, costs, a welcoming environment, and high-quality teaching are high priorities across the board for international students interested in Spanish universities.
What exactly constitutes high-quality teaching according to international students looking to study in Spain? The top three are:
- The university has received recognition of its teaching quality via a country-wide measurement scheme (63%)
- Up-to-date technology (62%)
- A high graduate employment rate (59%)
By focusing on these key decision-making factors, universities can enhance their appeal to international students. This can be achieved by investing in and highlighting modern technological facilities and resources, as well as amplifying high graduate employment rates in their recruitment offerings and promoting the unique strengths of their individual faculties to emphasise university reputation for successful career outcomes.
What concerns students looking to study in Spain?
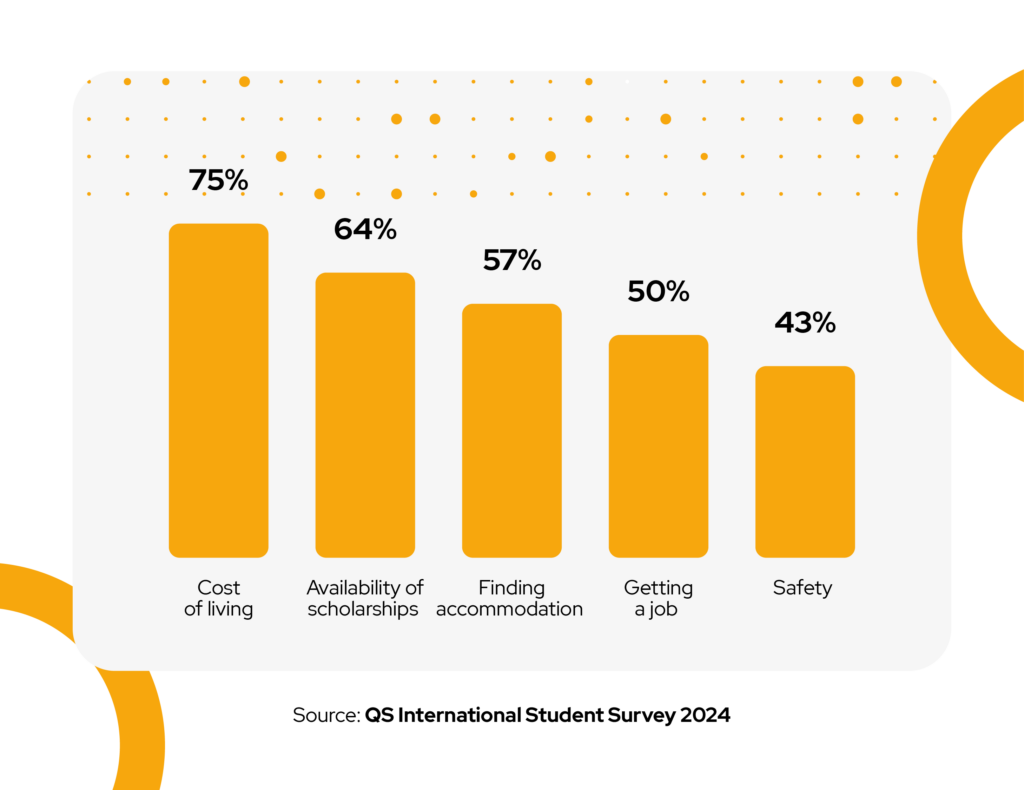
Again, the QS International Student Survey 2024 reinforces price sensitivity among international students, with ‘cost of living’ and scholarships receiving the highest number of responses. Additionally, the ability to work and live comfortably while studying is also crucial to them.
Spain’s performance in QS Best Student Cities 2025
Examining QS Best Student Cities 2025 data for Madrid and Barcelona, their rankings in the ‘Affordability’ indicator increased by 11 and six points respectively since the previous edition of the rankings, which may prove beneficial when prospective students assess their study options.
However, QS Best Student Cities 2025 also highlighted a decline in performance metrics compared to 2024. Madrid dropped seven spots overall, and Barcelona dropped three spots. Additionally, Madrid’s ‘Employer activity’ rank saw a notable decrease, and both cities experienced a drop in the ‘Student mix’ indicator.
As Spanish cities navigate the evolving landscape of student preferences and global competitiveness, QS insights underscore the significance of adapting to meet changing expectations.
Key strategies Spanish universities should implement to maintain their appeal as top destinations for international students include:
- Use affordability where possible – Highlighting the cost-effective nature of studying in Spain has significantly increased the appeal of cities like Madrid and Barcelona to students. Universities can further attract budget-conscious students by promoting their competitive tuition fees, available scholarships, and the overall lower cost of living compared to other European cities.
- Promote a welcoming environment – Universities can achieve this by actively promoting their support services for international students, such as language assistance, and cultural integration activities. Also, showcasing student testimonials and success stories can also help prospective students feel more confident about their decision to study in Spain.
- Understand and cater to expanding interests – With increasing interest from regions such as Asia-Pacific and Africa, identifying the specific needs and preferences of students through tailored marketing strategies, region-specific recruitment campaigns, and strong university partnerships with institutions from these areas can help attract a more diverse student body.



